Blog
Ghana is Ranked among Top 12 Countries with High Mortgage Interest Rates

A recent publication by the Centre for Affordable Housing Finance in Africa (CAHF) has spurred discussions around mortgage finance in Ghana and its implications for Ghana’s real estate sector. According to the publication, Ghana is counted among the top 12 countries within Sub-Saharan Africa with high mortgage interest rates.
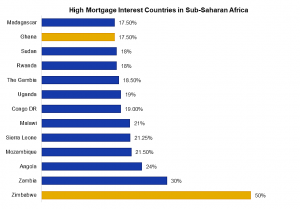
The statistic leaves so many questions on the minds of Ghanaians, specifically Ghanaians who have taken a keen interest in issues related to housing affordability. While some may wonder how mortgage interest rates and housing affordability are linked, the write-up seeks to explain basic concepts about mortgages within the African context and the implication of high-interest rates on housing affordability. Mortgage finance is a key component of housing affordability as it unlocks access to finance for the implementation of property development projects. However, in majority of countries within Sub-Saharan Africa (SSA), mortgages can only be accessed by a scanty proportion of
the population. Fuelled by lower household incomes and a general instability of income across Sub-Saharan African countries, the ability of mortgagees to pay back mortgage loans remains an issue of subjectivity.
In view of this, financial institutions in African countries impose stricter repayment terms to cover the risk involved in giving out mortgage loans. Acquiring finance for housing within the SSA region has been associated with high-interest rates, high down payment requirements and short repayment schedules.
In Ghana where about 80% of the entire population are employed within the informal sector, acquiring finance for housing is generally considered expensive. A key measure of the affordability of mortgages is the interest rate.
Implications of High Mortgage Rates
- High mortgage interest rates imply that the cost of acquiring capital for a real estate
development is high and increases the cost of development. - Where mortgage interest rates are high, potential purchasers of real property are
constrained as it decreases purchasing power in the real estate market. This generally
reduces housing affordability. - High mortgage rates could result in an oversupply of real estate assets with less
demand for the assets.
Author: Makafui Kuffo






